Times of crisis and opportunity
Responses to the crisis have drawn upon the innovative potential of businesses
The private sector has delivered a wide range of innovative solutions to help cope with the health emergency, and emerge from it as robustly as possible. Many firms have newly deployed or expanded their use of digital technologies to maintain their operations. The biopharmaceutical industry, often in partnership with academia, has launched hundreds of clinical trials targeting COVID-19 drugs and vaccines (see figure). Academic start-up companies have played significant roles in these efforts.
Registered COVID-19 vaccine and drug studies by economy
Number of COVID-19 studies, January to December 8, 2020
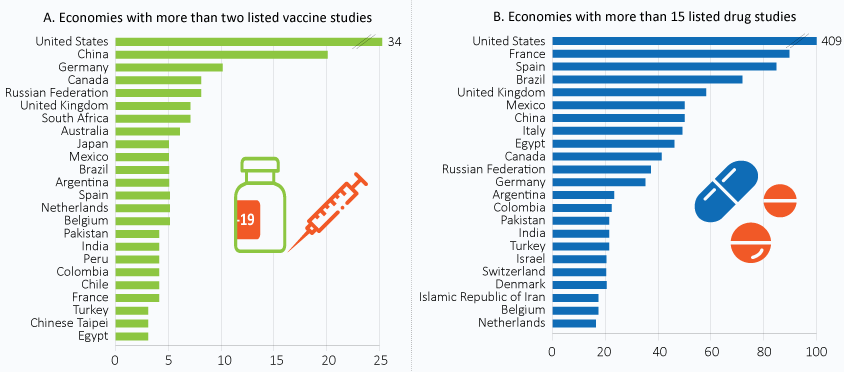
Source: United States National Institutes of Health, www.ClinicalTrials.gov (accessed 8 December 2020). StatLink https://doi.org/10.1787/888934223517
Another phenomenon observed during the first months of the pandemic was the rapid development of “frugal innovations” in response to shortages of medical equipment and other emergency supplies. The general public has also contributed through online fora and maker spaces, where engineers and scientists have successfully redesigned ventilators and other medical equipment to permit rapid production increases from locally available components. The need for such innovation will persist as countries face challenges in ramping up the production and distribution of vaccines.
Emerging technologies have important roles to play in tackling the pandemic and its impacts
Digital and biomedical technologies are playing essential and highly visible roles in combatting the pandemic’s impacts and finding medical solutions, particularly with regards to rapid vaccine development. Two emerging technologies, engineering biology and robotics, have shown promise in helping enhance the health resiliency of societies. Engineering biology attempts to turn biotechnology into a discipline more reminiscent of engineering than biology, and is more sharply focused on industrial production. A recent technological breakthrough, the biofoundry, can greatly reduce the time from idea to product, and improve the reliability and reproducibility of bio-manufacturing. Biofoundries are highly automated facilities that follow detailed, complex workflows through the co-ordinated use of laboratory robots. The messenger RNA vaccines for COVID-19 (e.g. the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines that have been the first to clear clinical trials) are especially amenable to this approach. Beyond their use in biofoundries, robotics can play other roles that enhance the health resiliency of societies, from aiding laboratory research, surgery and physical rehabilitation, to delivering medicines, transporting waste, combating loneliness and improving medical diagnostics and treatments. Governments possess several tools – including support to R&D and public-private partnerships – to accelerate the development and deployment of such technologies.
- Governments acted quickly to fund COVID-19-related research and innovation at scale
- The pandemic has triggered an unprecedented mobilisation of the scientific community
- Despite the disruption, scientists have continued their work during the crisis
- Responses to the crisis have drawn upon the innovative potential of businesses
- Business research and innovation have been impacted unevenly by the crisis
- Much of the research and innovation response to COVID-19 has been international
‹ Homepage
Related Documents
- Postgraduate training regimes need reforming to support a diversity of career paths
- The pandemic has triggered an unprecedented mobilisation of the scientific community
- Growing government debt could lead to austerity, and some hard choices for research and innovation policy
- Government R&D expenditures may need to shift to reflect new priorities
- Much of the research and innovation response to COVID-19 has been international
- Business research and innovation have been affected unevenly by the crisis
- Building government capabilities to meet future challenges will be a major challenge in itself
- Global challenges require global solutions
- Despite the disruption, scientists have continued their work during the crisis
- The STI policy mix needs to be more targeted
- Governments acted quickly to fund COVID-19-related research and innovation at scale