Health
Healthcare Quality and Outcomes Indicators
Healthcare quality is a core dimension of health system performance. Quality in healthcare means that the care provided is:
- Effective: achieving desirable outcomes, given the correct provision of evidence-based healthcare services to all who could benefit, but not to those who would not benefit
- Safe: reducing harm caused in the delivery of healthcare processes
- Patient-centred: placing the patient/user at the centre of its delivery of healthcare
DATA
In 2021, the OECD HCQO data collection process included a total of 64 indicators covering the following ‘themes’: Primary Care, Safe Prescribing in Primary Care, Acute Care, Mental Healthcare, Cancer Care, Patient Safety, and Patient Experiences. The collection reports data from 40 countries, including non-OECD member countries such as Singapore, Malta and Romania.
Health at a Glance 2023 also includes the first OECD reporting of quality indicators to capture:
- Integrated care
- End-of-life care
- Patient safety from the perspective of patients and healthcare workers
- Patient experience of care specific for patient receiving mental healthcare services
All indicators are available in the OECD Health Statistics database in the Healthcare Quality Indicators dataset in OECD.Stat:
| Healthcare Quality Indicators (full dataset) | Primary Care |
| Prescribing in Primary Care | Acute Care |
| Mental Healthcare | Patient Safety |
| Patient Experiences | Cancer Care |
Data and information on quality indicators for communicable diseases (screening and immunisation), cancer (screening and mortality) along with various other indicators related to lifestyle and prevention can be found:
- in the database OECD Health Statistics (see datasets listed above)
- in Chapter 6 on Quality and Outcomes of Care in Health at a Glance 2023: OECD Indicators
- and in Chapter 6 on Effectiveness: Quality of care and patient experience in Health at a Glance: Europe 2022
OECD Framework for Health System Performance Measurement
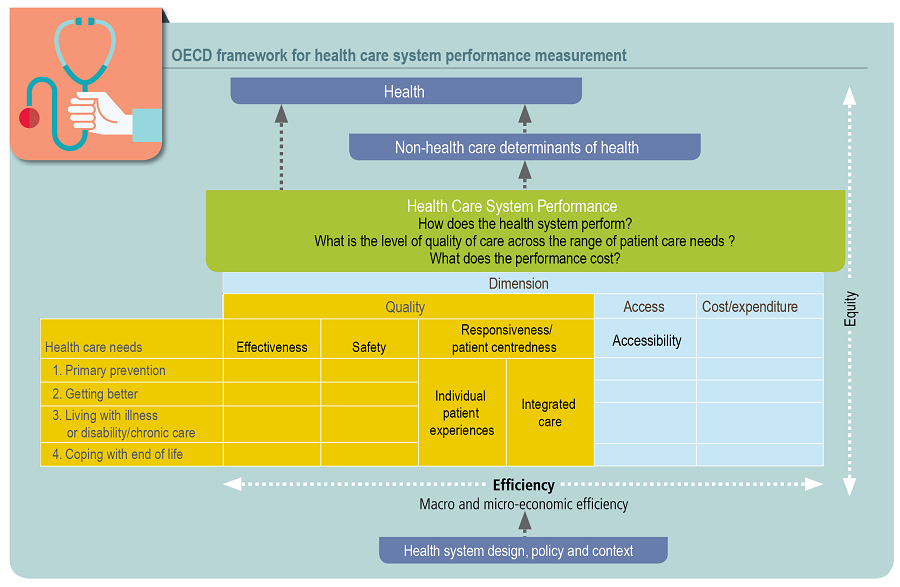
The Healthcare Quality and Outcomes programme previous known as Healthcare Quality Indicators (HCQI) Project was initiated in 2001. The aim was to develop and report indicators for international comparisons of healthcare quality. Over the past twenty years, data collection and analysis have been carried out, progressively expanding the coverage of the dimensions within the framework above and the number of countries involved. A continuous dialogue occurs between the OECD secretariat and a representative group of experts from OECD and non-OECD countries, international organisations including the World Health Organization and the European Commission and other relevant collaborating institutions, including universities, subject matter experts and research organisations.
FURTHER READING
- Visit our page gathering all Health Working Papers to find the latest work on Healthcare Quality and Outcomes
- F. Carinci, K. Van Gool, J. Mainz, J. Veillard, E. C. Pichora, J. M. Januel, I. Arispe, S. M. Kim, and N.S. Klazinga, on Behalf of The OECD Health Care Quality Indicators Expert Group (2015), “Towards actionable international comparisons of health system performance: expert revision of the OECD framework and quality indicators”, International Journal for Quality in Health Care, Vol. 27/2, pp. 137-146
- The original OECD Health Care Quality Framework (OECD Health Working Paper No. 23, March 2006)
- O. Arah, G. Westert, J. Hurst, and N. Klazinga (2006), “A conceptual framework for the OECD Health Care Quality Indicators Project”, International Journal for Quality in Health Care, Vol. 18/suppl_1, pp. 5-13
- (2010)
- Healthcare Quality and Outcomes
- Health Statistics
- Health Publications
CONTACT US
- Ms. Katherine de Bienassis: katherine.debienassis@oecd.org
- Ms. Eliana Barrenho: eliana.barrenho@oecd.org
- Ms. Rie Fujisawa: rie.fujisawa@oecd.org
- Mr. Gabriel Di Paolantonio: gabriel.dipaolantonio@oecd.org
- Generic contact: hcqo.contact@oecd.org
 Follow us on Twitter via @OECD_Social
Follow us on Twitter via @OECD_Social
Related Documents