Industry and globalisation
Employment and Global Value Chains (GVCs)
Measuring the impact of foreign demand on domestic labour markets
Last updated: January 2024
Growing economic integration worldwide and the spread of global value chains (GVCs) increases the sensitivity of employment in one country or region to changes in demand in other countries or regions. However, traditional statistics do not reveal the full nature of global interdependencies - notably how consumption in one country may drive production and, therefore, sustain employment in economies further up the value chain. OECD’s Inter-Country Input-Output (ICIO) Database, developed primarily to produce indicators of Trade in Value Added (TiVA), also allows indicators to be developed that can provide insights into the origins of demand driving a country’s employment. Estimates of employment sustained by foreign final demand (or by exporting activities) can reveal the extent to which a country’s workforce depends on its integration into the global economy.
Trade in employment (TiM) indicators
The Trade in employment (TiM) Database presents indicators of employment by industry, consistent with output and value added in the TiVA database, for all OECD, European Union and G20 countries. All 45 TiVA industries are covered for the time-period 1995-2020.
- Further information is available in the OECD Science, Technology and Industry Working Paper "Measuring employment in global value chains".
The results presented here are based on the 2023 edition of the ICIO Database.
- Access to Trade in employment 2023 edition
- Access to Country data sources
In 2020, for example, between 30% and 60% of business sector employment in most European countries was sustained by consumers in foreign markets (though predominantly within Europe – a consequence of regional economic integration). For some smaller European countries, this share reached over 70%. In Japan and the United States, shares are lower, reflecting their relatively large size and lower dependency on exports / imports. In spite of this, estimates suggest that in 2020 the number of jobs sustained by foreign demand reached over 11 million in the United States and almost 8 million in Japan.
Employment in business sector sustained by foreign final demand, by region of demand, 2020
As a percentage of total business sector employment
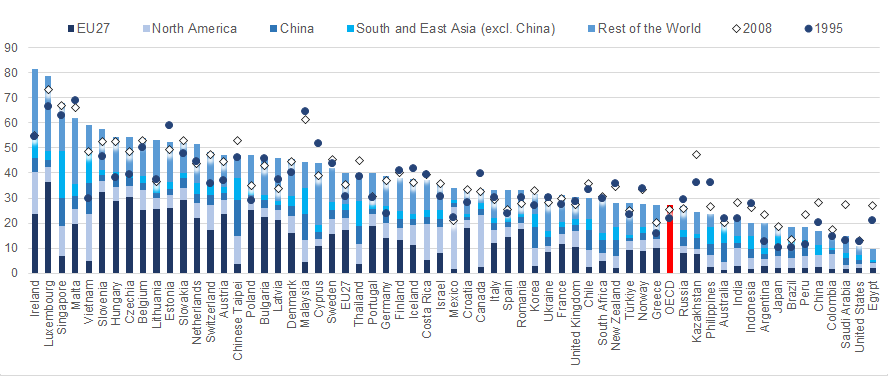
Source: OECD, Trade in Employment Database (TiM), 2023.
Note: OECD and EU27 averages include intra-regional flows; these figures should be considered as weighted averages of their member countries.
Business sector is defined as Non-agriculture business sector excluding Real estate; it corresponds to ISIC Revision 4 Divisions 05 to 39, 41 to 43, 45 to 56, 58 to 63, 64 to 66 and 69 to 82.
Related links
- Trade in Value Added (TiVA)
- Inter-Country Input-Output (ICIO)
- CO2 embodied in international trade (TeCO2)
- Multinational entreprises and GVCs
Other editions of TiM
- Trade in employment 2021 ed. (1995-2018, 45 ISIC rev.4 industries)
- Trade in employment 2019 ed. (2005-2015, 36 ISIC rev.4 industries)
- Trade in employment 2016 ed. (1995-2011, 34 ISIC rev.3 industries)
Contact
Any suggestions or queries can be sent to stan.contact@oecd.org mentioning Trade in Employment (or TiM) in the title of your message.
Related Documents