Publications

Adults, Computers and Problem Solving
What's the Problem?
The report provides an in-depth analysis of the results from the Survey of Adult Skills
related to problem solving in technology-rich environments, along with measures concerning
the use of ICT and problem solving. The Nordic countries and the Netherlands have
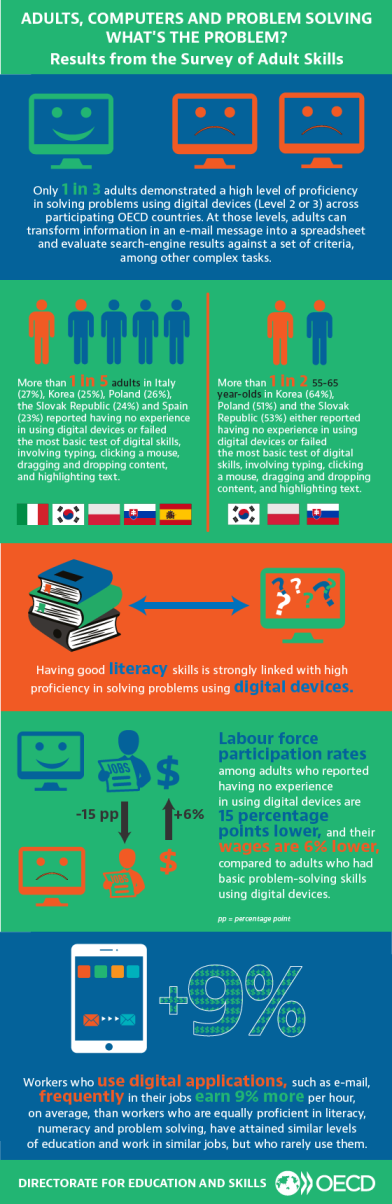
the largest proportions of adults (around 40%) who score at the higher levels in problem
solving, while Ireland, Poland and the Slovak Republic have the smallest proportions
of adults (around 20%) who score at those levels. Variations in countries’ proficiency
in problem solving using ICT are found to reflect differences in access to the Internet
and in the frequency with which adults use e-mail. The report finds that problem-solving
proficiency is strongly associated with both age and general cognitive proficiency,
even after taking other relevant factors into account. Proficiency in problem solving
using ICT is related to greater participation in the labour force, lower unemployment,
and higher wages. By contrast, a lack of computer experience has a substantial negative
impact on labour market outcomes, even after controlling for other factors. The discussion
considers policies that promote ICT access and use, opportunities for developing problem-solving
skills in formal education and through lifelong learning, and the importance of problem-solving
proficiency in the context of e-government services.
Published on June 23, 2015Also available in: French
In series:OECD Skills Studiesview more titles
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Foreword and Acknowledgements | |
| Executive Summary | |
| About The Survey of Adult Skills | |
| Reader's Guide | |
| Problem solving in technology-rich environments and the Survey of Adult Skills | |
| Proficiency in problem solving in technology-rich environments | |
| Differences within countries in proficiency in problem solving in technology-rich environments | |
| Proficiency in problem solving in technology-rich environments, the use of skills and labour market outcomes | |
| Some pointers for policy | |
Powered by OECD iLibrary