Health at a Glance: Europe 2022

State of Health in the EU Cycle
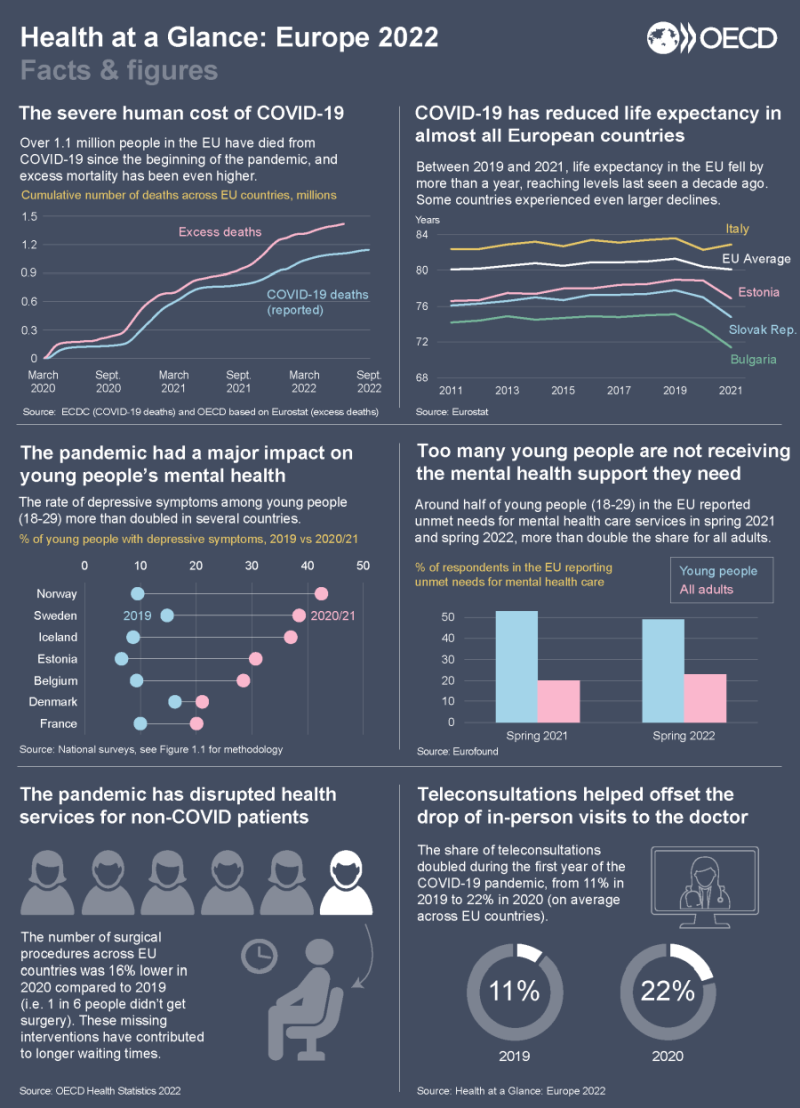
This new edition of Health at a Glance: Europe reviews key challenges to build more resilient and effective health systems following COVID-19. A special focus is put on the impact of the pandemic on young people’s mental and physical health. The report also assesses the pandemic impact in disrupting care for non-COVID patients and the policy responses to minimise adverse consequences.
READ MORE
Indicators by theme

Coping with COVID: Young people’s health
The pandemic had a significant impact on young people’s physical and mental health, with depression symptoms increasing greatly and young people spending less time in physical activity.
©OECD
LEARN MORE...
Service disruption during the pandemic
The pandemic disrupted care for non-COVID patients (primary care, mental health care, cancer care, chronic care and elective surgery), generating backlogs and increasing waiting times.
©OECD
LEARN MORE...
Life expectancy and chronic diseases
The pandemic resulted in unprecedented reductions in life expectancy in many EU countries in 2020 and 2021. EU countries must also continue to prepare to face the “epidemic” of chronic diseases.
©OECD
LEARN MORE...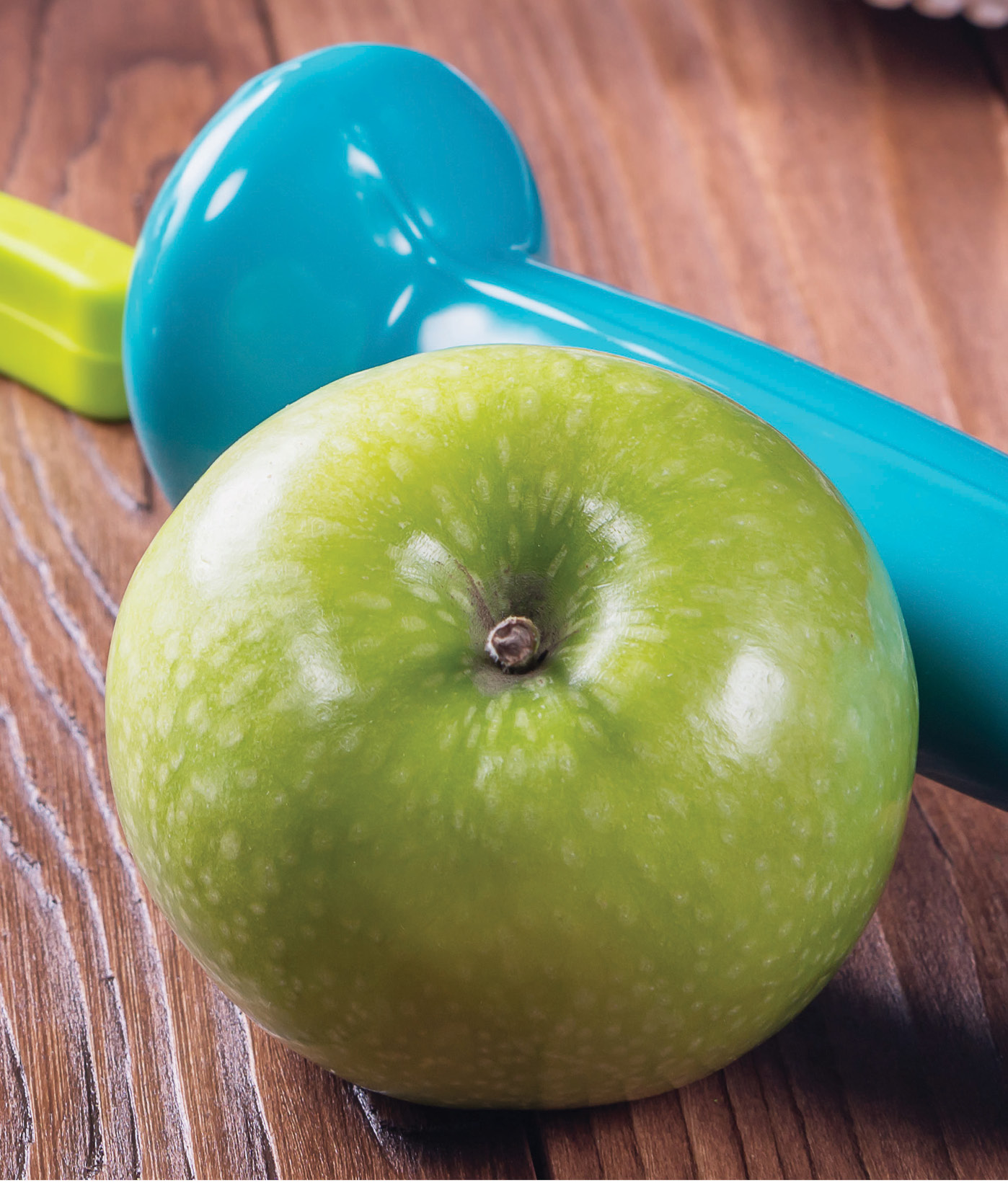
Smoking, alcohol and obesity
Modifiable risk factors to health, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, unhealthy nutrition, lack of physical activity and obesity, contribute greatly to the burden of chronic diseases and premature mortality.
©OECD
LEARN MORE...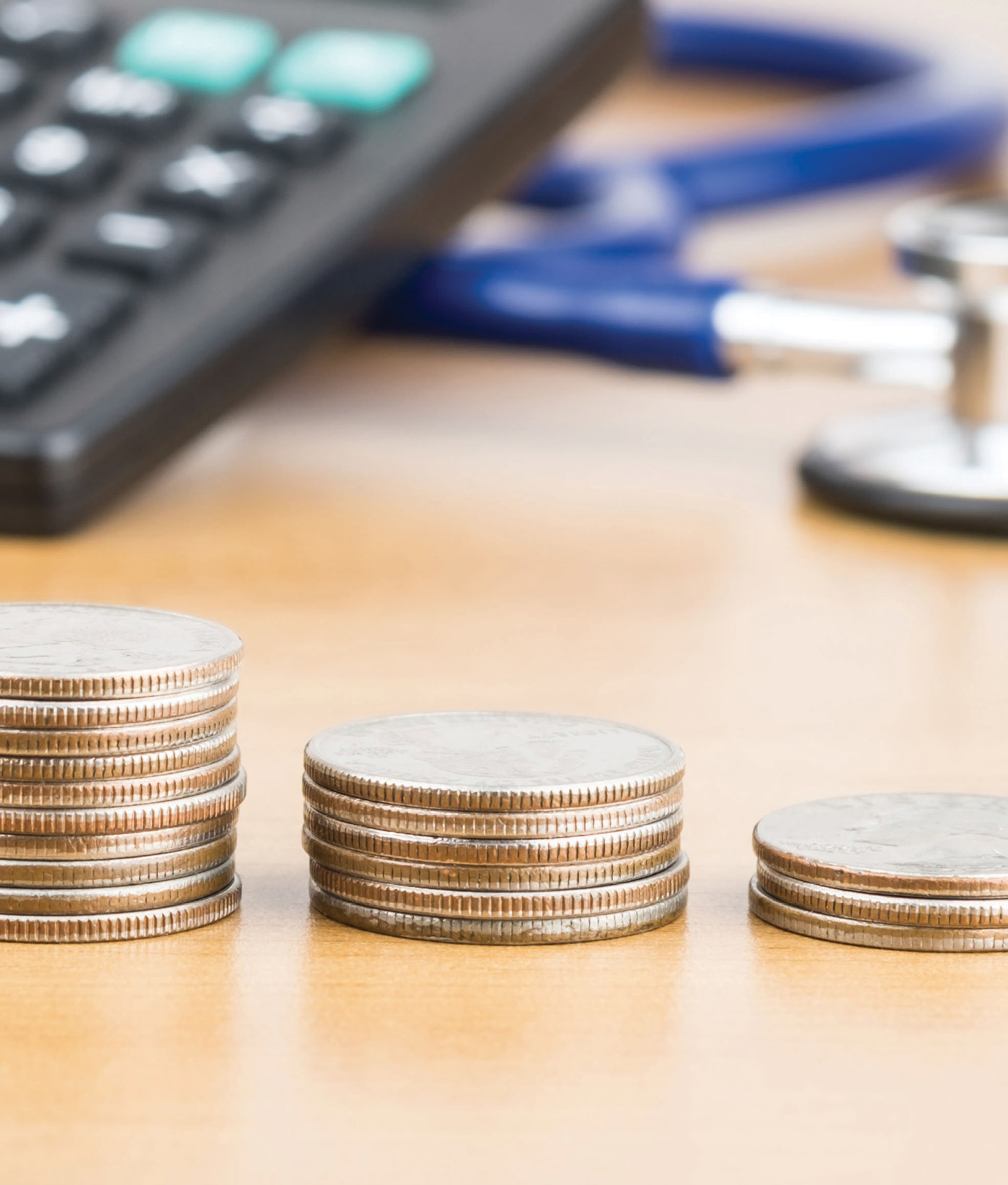
Health spending
Health spending increased significantly in most countries to address the consequences of the pandemic. Spending on health as a share of GDP went up to 10.9% in the EU in 2020, partly due also to GDP reduction.
©OECD
LEARN MORE...
Quality of care and patient experience
Delays in cancer screening during the pandemic have resulted in people being diagnosed at a more advanced stage. One of the positive consequences of the pandemic has been the increase in vaccination rate against seasonal flu among older people and other vulnerable groups.
©OECD
LEARN MORE...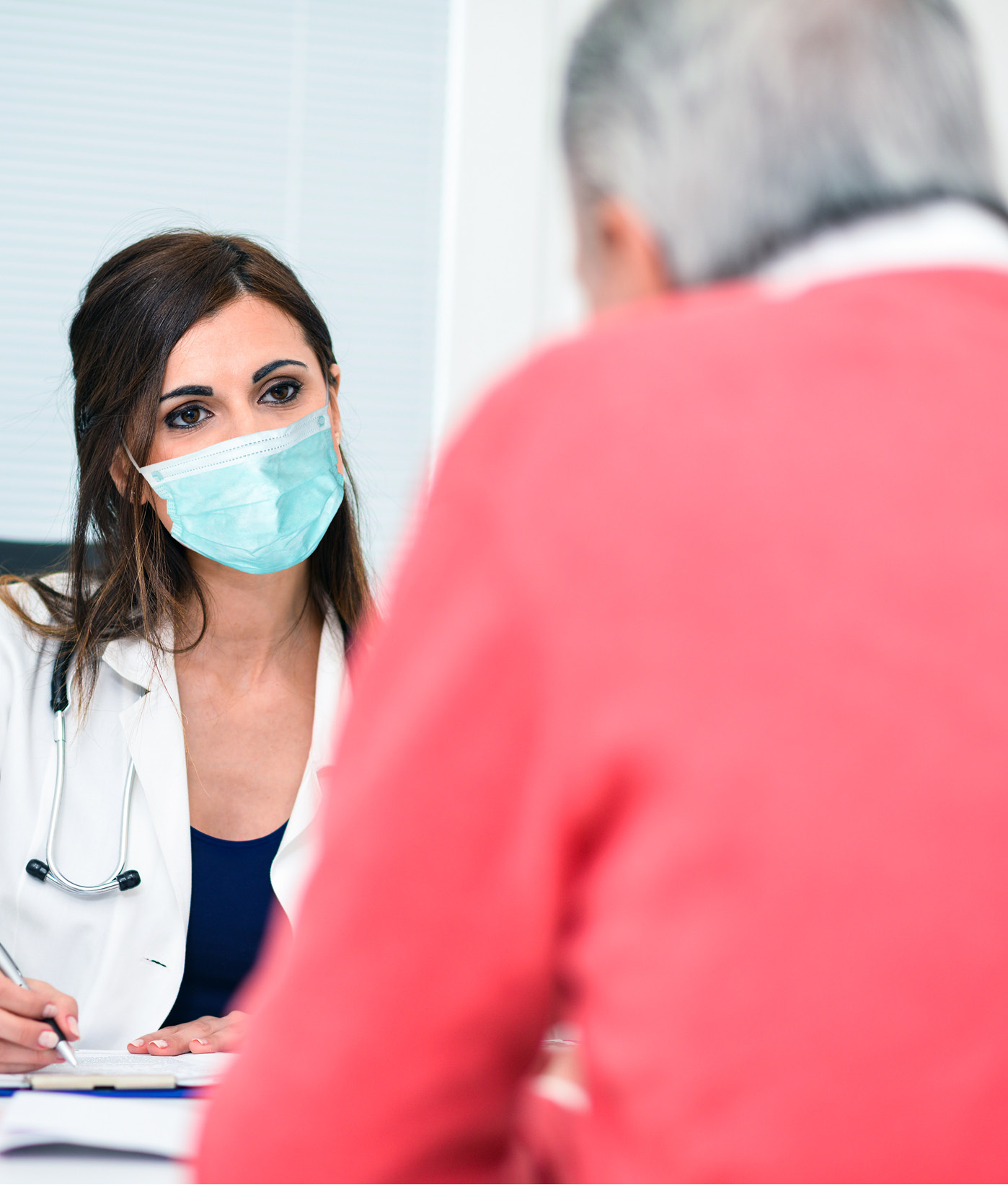
Affordability and availability
Most EU countries have universal health coverage, but the range of services covered and degree of cost-sharing vary. Effective access can be restricted by health workforce shortages, waiting times or geographic barriers.
©OECD
LEARN MORE...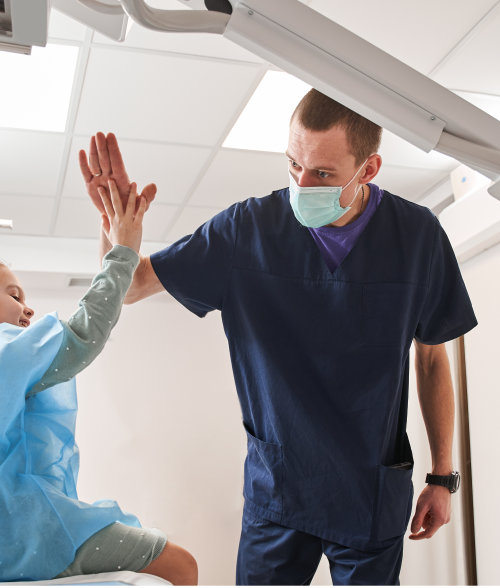
Resilient health systems
The response of health systems to the COVID-19 crisis offers insights into their resilience. Those responses included new methods of safely delivering care with a doubling of the share of teleconsultations, and the rapid delivery of vaccinations.
©OECD
LEARN MORE...More information
Related links
|
CONTACT US
 Follow us on Twitter via @OECD_Social
Follow us on Twitter via @OECD_Social