Environment

Diffuse Pollution, Degraded Waters
Emerging Policy Solutions
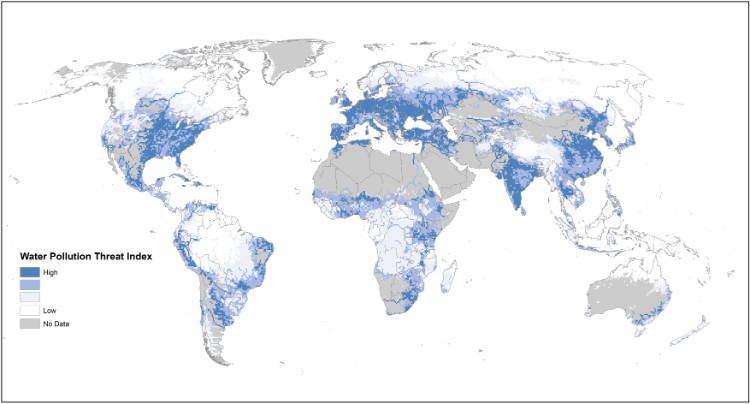
After decades of regulation and investment to reduce point source water pollution,
OECD countries still face water quality challenges (e.g. eutrophication) from diffuse
agricultural and urban sources of pollution, that is disperse pollution from surface
runoff, soil filtration and atmospheric deposition. The relative lack of progress
reflects the complexities of controlling multiple pollutants from multiple sources,
their high spatial and temporal variability, associated transactions costs, and limited
political acceptability of regulatory measures. This report outlines the water quality
challenges facing OECD countries today, presents a range of policy instruments and
innovative case studies of diffuse pollution control, and concludes with an integrated
policy framework to tackle diffuse water pollution. An optimal approach will likely
entail a mix of policy interventions reflecting the basic OECD principles of water
quality management – pollution prevention, treatment at source, the polluter pays
and beneficiary pays principles, equity, and policy coherence.
Published on March 22, 2017
In series:OECD Studies on Waterview more titles
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Foreword and Acknowledgements | |
| Acronyms and Abbreviations | |
| Executive summary | |
| The Water Quality Challenge | |
| An overview of the main water pollutants in OECD countries | |
| Economic costs and policy approaches to control diffuse source water pollution | |
| Emerging policy instruments for the control of diffuse source water pollution | |
| A policy framework for diffuse source water pollution management |
Powered by OECD iLibrary