Development finance topics
OECD Social Impact Investment Initiative
| Social impact investing provides finance to organisations addressing social and/or environmental needs with the explicit expectation of a measurable social, as well as financial, return. It thus aims to foster economic development while achieving social outcomes. It is one way of channelling more resources towards the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). |
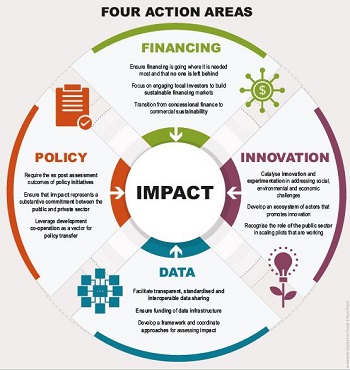
Impact Standards for Financing Sustainable DevelopmentThese Impact Standards for Financing Sustainable Development have been developed by the OECD and UNDP in close consultation with practitioners in the context of the DAC Community of Practice on Private Finance for Sustainable Development. They are grounded in high-level impact management principles and can be used alongside other tools and frameworks by donors, development finance institutions and private actors seeking to have real and positive impacts on the achievement of the SDGs. A voluntary and freely available public good, the Impact Standards are designed to help public and private investors build stronger systems to understand and critically evaluate their impact – both positive and negative on people and planet.
|
The 2019 OECD publication Social Impact Investment: The Impact Imperative for Sustainable Development brought new evidence on the role of SII in financing sustainable development and provided recommendations for delivering on the “impact imperative” of financing sustainable development.
|
Related Documents