Centre for Entrepreneurship, SMEs, Regions and Cities

The Culture Fix
Creative People, Places and Industries
Cultural and creative sectors and industries are a significant source of jobs and
income. They are a driver of innovation and creative skills, within cultural sectors
and beyond. They also have significant social impacts, from supporting health and
well-being, to promoting social inclusion and local social capital. As national and
local governments reconsider growth models in the wake of COVID-19, cultural and creative
sectors can be a tool for a resilient recovery if certain longer-term challenges in
the sector are addressed. The report outlines international trends with new data,
including at subnational scale. It addresses issues in cultural and creative sectors
in terms of employment, business development, cultural participation and funding,
both public and private. It provides analysis of how these sectors contribute to economic
growth and inclusion, taking into account the impact of COVID-19 related crisis on
jobs and firms. Finally, it offers recommendations on how to capitalise on the role
of cultural and creative sectors in national and local recovery strategies.
Available from June 03, 2022
In series:Local Economic and Employment Development (LEED)view more titles
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Preface by the OECD | |
| Foreword | |
| Executive summary | |
| Report in brief | |
| Defining and measuring cultural and creative sectors | |
| Cultural participation as a driver of social and economic impact | |
| Cultural and creative jobs and skills: who, what, where, and why it matters | |
| Sectoral perspectives: Music and museums | |
| Entrepreneurship and business development in cultural and creative sectors | |
| Regional perspectives: CCS as drivers of regional and local development | |
| Public and private funding for cultural and creative sectors | |
| Regional Perspectives: Using culture and creativity to transform places | |
| Sectors included in employment and business statistics by country | |
| Glossary of terms | |
Powered by OECD iLibrary
Key messages
Culture as a driver of employment
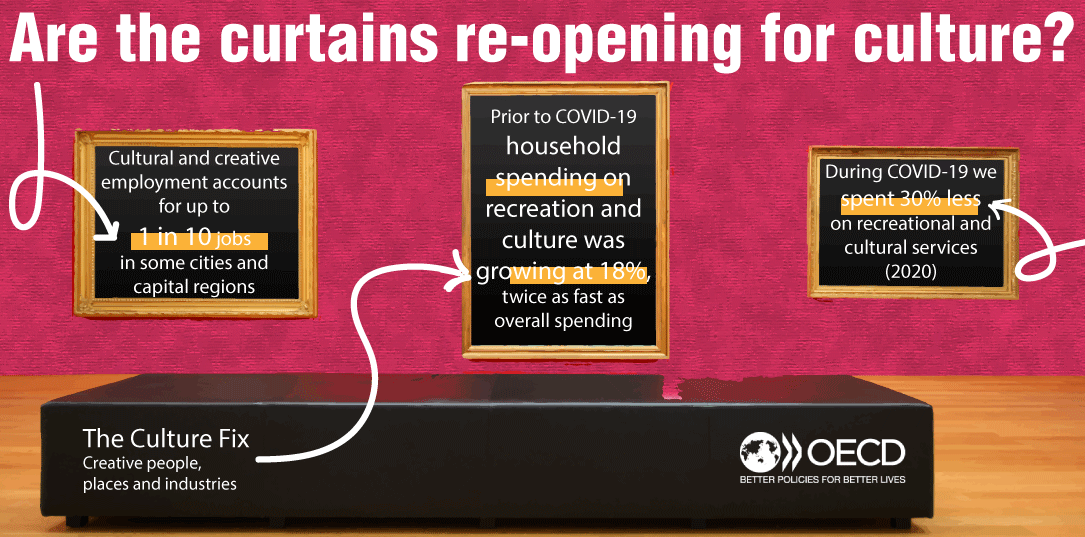
Cultural and creative employment account for up to 1 in 20 jobs in some OECD countries,
and up to 1 in 10 jobs in major cities. These jobs are “future proof” (10% at high
risk of automation vs. 14% in general workforce).
Culture as a driver of business growth
Cultural and creative sectors represent an average of 7% of all enterprises in OECD
countries, and outpaced growth in the business economy (18% compared to 12% on average
across OECD) prior to COVID-19 crisis.
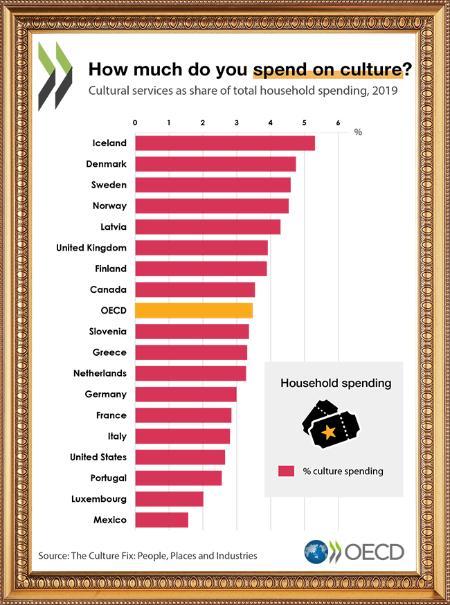
Culture as a driver of consumption
While household spending on recreation and culture grew by 18% between 2011 and 2019,
outpacing overall spending; it dropped by about 30% in 2020 relative to 2019 as a
result of the COVID-19 crisis.