South Africa
 OECD recommendations
OECD recommendations
Labour productivity has declined since 2011. To boost productivity and inclusion, ensure more market competition, in particular in network sectors, strengthen the management of state-owned enterprises, reduce red tape and access barriers and improve the education system.
- Foster on‑the‑job training with tax credits and by expanding apprenticeship programmes.
- Complete the introduction of independent network-industry regulators.
- Use more regulatory impact analysis to reduce the regulatory burden, eliminate entry barriers, and promote competition.
- Privatise state-owned companies, such as telecoms, that are in markets that could be competitive.
- Establish a public employment service as a one-stop shop for job seekers.
- Expand affordable public transport and build new, denser housing closer to economic centres.
 Data
Data
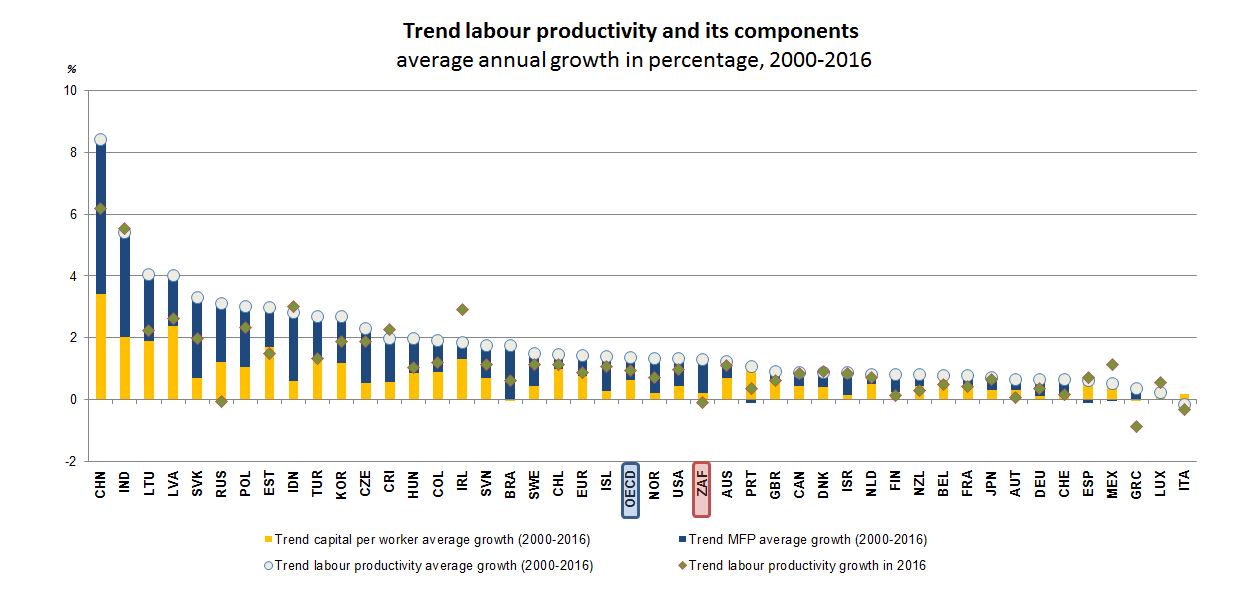
Source: OECD May 2017 Economic Outlook database.
 Key publications
Key publications
OECD (2015), "More effective infrastructure and business regulation", in OECD, OECD Economic Surveys: South Africa 2015, OECD Publishing, Paris.
Fedderke, J.W. (2013), “South Africa’s Growth Performance” in H. Bhorat et al (eds), The Oxford Companion to the Economics of South Africa, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 39-50.
Klein, N. (2012), "Real Wage, Labor Productivity, and Employment Trends in South Africa: A Closer Look", International Monetary Fund WP/12/92.
National Planning Commission (2011), The National Development Plan (NDP).
 Productivity - enhancing institutions
Productivity - enhancing institutions
The National Planning Commission was established in 2010 to develop a long term vision and strategic plan for South Africa. It is tasked with producing research on cross-cutting issues to provide evidence and recommendations to the government. The 24 part-time external commissioners were drawn from public nominations and chairperson and deputy chairperson are appointed by the president.
Productivity SA was established as a public entity in 1969 and rebranded in 2007. Its mandate is to enhance the productive capacity of all South Africans and key activities include running programmes such as providing technical assistance to companies and organisations. Its board comprises members from labour, government and business.
Related Documents

