Principle 7
Effective organisational & governance coordination framework
Key Issues
|
 |
Overview
The optimum use of digital technologies depends on the framework in place.
A framework should:
- Establish a clear body/unit responsible for co-ordinating ICT roll-out with a key mandate to steer change,
- Ensure coherence of main relevant strategies
- Develop common policies and standards
- Drive the adoption of national interoperability frameworks for data exchange
- Facilitate synergies and sharing of lessons across policy domains.
Risks of poor coordination:
- Poor information flow and cooperation across government
- Public sector fragmentation
- Uneven preparedness to use ICTs
Reviews are important:
- Governments should periodically review their governance architectures
- Redesigns may be necessary to break down silos
- Governments should adopt flexible structures
Frameworks should enable the:
- Pooling of resources and services
- Re-engineering of processes
- Adoption of common standards that support high integration
- Interoperability of systems and service-oriented architectures
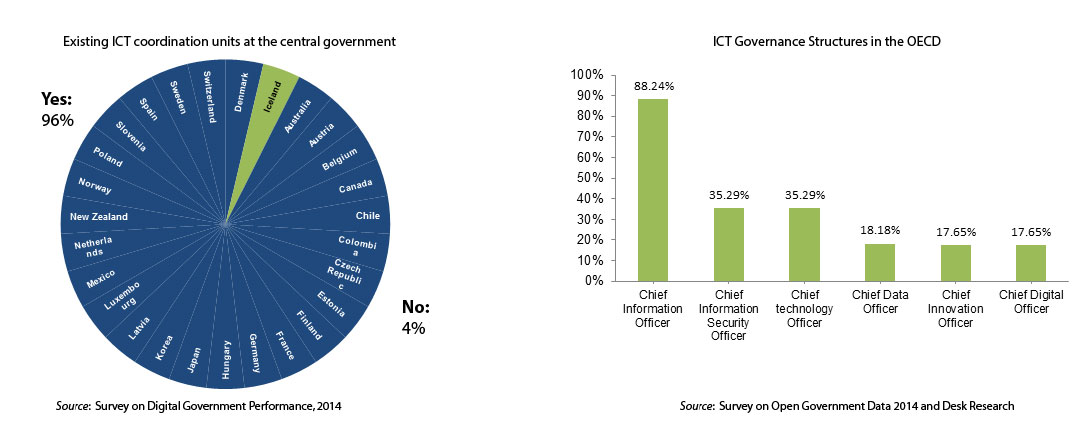
Data
Good practices
Canada
Principle 7 - My VAC Book
chile
Principle 7 - Strengthening of Digital Government Governance
colombia
Principle 7 - IT Leadership – Implementation of the CIO Role in the Public Administration
Principle 7 - Excellence and Appropriation Centres on Big Data, Data Analytics
Principle 7 - Route of Excellence
finland
Principle 7 - Enterprise Architecture in the Public Sector
italy
Overall - 3 Year ICT Plan
japan
Principle 7 - Innovative Working Environment
mexico
Principle 7 - National One-Stop Portal
Principle 7 - National Digital Strategy
Principle 7 - Interministerial Commission for the Development of Electronic Government
portugal
Principle 7 - Global Strategic Plan for Rationalization of ICT Costs in Public Administration (PGETIC)
slovenia
Principle 7 - IT Reorganization in Public Administration
new zealand
Principle 7 - Better Public Service Programme – Result 10
Principle 7 - Better Public Services Programme – Result 9
Principle 7 - Partnership Framework
Sweden
Principle 7 - Verksamt.se

