Regulatory policy
The Governance of Regulators
 |
As one of the main actors in regulatory policy, regulators have an important and increasingly complex role in the delivery of regulatory regimes and regulations. The governance arrangements for regulators are a key factor in a regulator’s ability to operate effectively to achieve the social, environmental and economic outcomes it is responsible for.
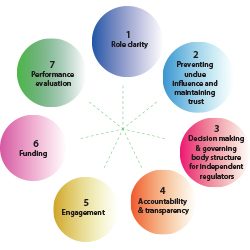
The OECD Best Practice for Regulatory Policy: The Governance of Regulators detail the key principles for establishing and operating regulatory agencies. They also provide more detailed considerations that should be reflected upon to apply the principles to different cultural and political contexts. The seven governance principles for regulators are: |
|
The 2012 Recommendation of the Council on Regulatory Policy and Governance recognises that an effective regulatory policy includes “a consistent policy covering the role of functions of regulatory agencies in order to provide greater confidence that regulatory decisions are made on an objective, impartial and consistent basis, without conflict of interest, bias or improper influence.”
The OECD Best Practice Principles for Regulatory Policy: The Governance of Regulators have an informal status of guidance approved by the Regulatory Policy Committee and OECD Network of Economic Regulators. They can be used by member and non-member countries to guide their reforms. The Principles will also be used by the Secretariat when reviewing regulatory policies in member and non-member countries as a set of evaluation criteria. |
 |
KEY PUBLICATIONS
- OECD Best Practice Principles for Regulatory Policy: The Governance of Regulators (2014) - English / French / Flyer
- OECD Best Practice Principles for Regulatory Policy: Regulatory Enforcement and Inspections (2014) - English / French
- Governance of Regulators' Practices: Accountability, Transparency and Co-ordination (2016) - English
- Being an Independent Regulator (2016) - English
- Governance of Regulators' Practices: Accountability, Transparency and Co-ordination - Case Studies for Mexico (2017) - English
- The Role of Economic Regulators in the Governance of Infrastructure (2017) - English
- Creating a Culture of Independence, Practical Guidance against Undue Influence (2017) English / French / Spanish
- Creating a Culture of Independence, Practical Guidance against Undue Influence (2017) (Brochure) English / French / Spanish
- Ireland's Commission for Regulation of Utilities (2018) - English
COUNTRIES AND REGULATORS BUILDING ON THE PRINCIPLES
- Victoria State Government, Review of Victoria's Electricity and Gas Network Safety Framework (2018)
- Victoria State Government, Independent Inquiry into the Environment Protection Authority (2016)
- European Regulators Group for Audiovisual Media Services (ERGA), ERGA Report on the independence of National Regulatory Authorities (December 2015)
- Review of Governance Arrangements for Australian Energy Markets (October 2015)
- Australian Productivity Commission, Mutual Recognition Schemes (September 2015)
- Improving Economic Regulation of Urban Water: A report prepared for the Water Services Association of Australia (August 2014)
- Australian National Audit Office, Best Practice Guide: Administering Regulation: Achieving the Right Balance (June 2014)
CONTACT
For further information, please contact Anna Pietikainen.
MORE ABOUT
Related Documents