Centre for Entrepreneurship, SMEs, Regions and Cities

Understanding Firm Growth
Helping SMEs Scale Up
Few small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) scale up, but these few fast growing
firms are the major driver of new jobs added to OECD economies. This report helps
policy makers get a grip on growth of those few SMEs by considering the transformation
they undergo before, during and after their high-growth phase. Based on analysis of
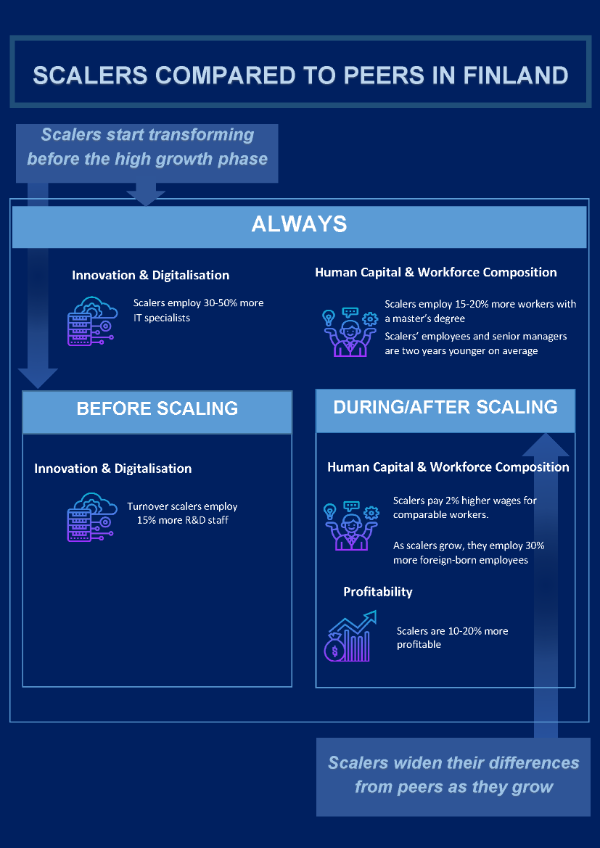
detailed firm-level data in a pilot project implemented for Finland, Italy, Portugal,
the Slovak Republic and Spain, the report shows that SMEs in all types of places,
of all ages and in all sectors have the potential to scale up. The strength of the
potential does, however, vary. Getting a grip on growth of SMEs can pay important
dividends as scalers contribute the majority of new jobs created by SMEs during their
high-growth phase, but also continue to contribute positively to aggregate job creation
and aggregate growth in turnover in the following years. A closer look at the characteristics
of SMEs that scale up compared to similar “peers” that do not, shows that scaling
is likely a strategic choice and includes investments and other preparatory transformation
in the years preceding scaling up.
Published on November 17, 2021
In series:OECD Studies on SMEs and Entrepreneurshipview more titles
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Foreword | |
| Executive summary | |
| The knowledge gap on scalers | |
| How do scalers contribute to economic growth? | |
| Which SMEs scale up? | |
| How do scalers transform as they grow? | |
| Additional charts and tables | |
| National firm-level data sources | |
| Methodological notes |
Powered by OECD iLibrary