Science, technology and innovation policy
Green growth and eco-innovation
Latest news | Work in 2011-12 | Background
Framework, practices and measurement: key findings
| Documents | Related websites | Contact
Permanent URL of this page: www.oecd.org/innovation/green
Innovation in technologies and how they are applied are key to enabling industry to create new business values while also benefiting people and the planet. In recent years, manufacturing companies have been upgrading their efforts towards sustainable manufacturing from pollution prevention to integrated approaches that take into account product lifecycles and wider impacts. Eco-innovation helps to enable this evolution through a combination of technological and non-technological changes that can yield substantial environmental improvements. The current economic crisis and climate change negotiations should be taken as a great opportunity to move towards a green economy by accelerating eco-innovation.
|
Latest news |
OECD Green Growth Paper: Market Development for Green Cars
This report presents and analyses policies, programmes and approaches for the development, market introduction and diffusion of green cars. It reviews government policies in a number of OECD countries as well as a selection of non-OECD economies. The report attempts to provide: i) a better understanding of the growing market for green vehicles; ii) new analytical instruments to identify policies and approaches that could be designed and put in place, notably with the aim of fostering the uptake of green cars; and iii) to the extent possible, insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of existing policies, as well as guidance on how to assess the impact of future measures.
OECD/European Commission/Nordic Innovation Joint Workshop
The Future of Eco-Innovation: The Role of Business Models in Green Transformation
Firms and entrepreneurs are exploring green business opportunities, increasingly based on systemic thinking and radical innovations, aiming to capture and create value from new business models. Both the OECD and Nordic Innovation (NI) are currently conducting business case studies on business model-based eco-innovation. This workshop aimed to showcase good practices from these studies and to enhance understanding of the role that new business models can play, as well as to establish a network of experts and innovators in this area. Over 160 people including 50 presenters gathered in Copenhagen on 19-20 January 2012 and established a network of innovators, experts and policy makers for promoting new ways to enhance green growth opportunities. Click here for the workshop presentations and background materials.
OECD Sustainable Manufacturing Toolkit
|
|
The OECD Sustainable Manufacturing Toolkit is designed to help businesses around the world, particularly supply chain firms and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), develop a more viable, socially responsible business approach and make the most of green growth opportunities. It provides a set of 18 internationally applicable, common and comparable key performance indicators to measure and improve the environmental performance of manufacturing facilities. This indicator framework owes to much to the existing variety of environmental and CSR initiatives and offers a potential for future standardisation in this area. For any businesses which are looking to tackle sustainability – what it means, how it relates to their business, and how they can benefit from greener production – the OECD Sustainable Manufacturing Toolkit is a great place to start! The Toolkit incldes a start-up guide (image left), which provides a step-by-step approach to measuring and benchmarking environmental performance, and a web portal (www.oecd.org/innovation/green/toolkit) which provides additional technical guidance, data tools and useful links. |
|
Work in 2011-12 |
In the current economic crisis, eco-innovation is gaining ground within both industry and government as an effective way to tackle climate change and to foster green growth. The second phase of this project aims to better understand highly complex nature of such innovations and guiding policy makers and industry practitioners for putting more innovative solutions into practice. The outcomes of this project will form an integral part of the OECD Green Growth Strategy.
The second phase consists of four modules:
a) Case studies of new business approaches to eco-innovation,
b) Analysis and case studies of policies to drive eco-innovation,
c) Empirical analysis of eco-innovation and the transition in industrial structure required to realise green growth,
d) Development of an indicator toolkit to help realise sustainable manufacturing in firms (Sustainable Manufacturing Toolkit).
In each module, we are engaging relevant stakeholders and experts for their input through a member-only community website. If you are interested, please contact us.
Improving resource and energy use and engaging in a broad range of innovations to improve environmental performance will lead to new industries and new jobs in coming years. Incremental improvement is not enough, however. Industry must be restructured, and existing and breakthrough technologies must be more innovatively applied to realise green growth. Short-term relief packages deployed today can stimulate investments in technologies and infrastructures that help innovation and enable changes in the way we produce and consume goods and services.
In this context, the OECD Project on Green Growth and Eco-innovation was launched in 2008 with an initial aim to better understand how innovation can result in new technological and systemic solutions to global challenges and to provide industry with a means to improve their contributions to sustainable development.
|
Framework, practices and measurement: key findings from Phase I |
The first phase of the project focused on the development of an analytical framework and a review of the state of current knowledge on industry practices, policy initiatives and measurement. The overall findings are:
-
The evolution of sustainable manufacturing has been realised through both technological and non-technological eco-innovations.
-
Improvement in indicators and measurement can accelerate corporate efforts and deepen understanding of eco-innovation by industry and policy makers alike.
-
Better understanding of the right levers for eco-innovation from both supply and demand side is needed for developing an effective policy mix.
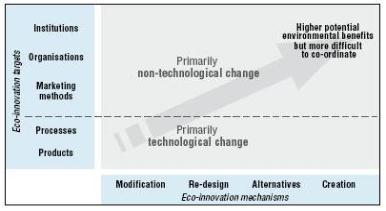 |
Eco-innovation has three dimensions: its targets (the main focus), its mechanisms (methods for introducing changes in the target) and its impacts (the effects on environmental conditions). Eco-innovation also involves both technological and non-technological changes. |
|
|
Further reading: Eco-Innovation in Industry: Enabling Green Growth
This book reviews the concepts and forms an analytical framework of eco-innovation; analyses the nature and processes of eco-innovation; discusses existing sustainable manufacturing indicators; examines methodologies for measuring eco-innovation; and takes stock of national strategies and policy initiatives for ecoinnovation. This is part of the OECD Innovation Strategy series and the first contribution to the OECD Green Growth Strategy. |
|
|
Fostering Innovation for Green Growth
Innovation is key to green growth. It helps decouple growth from natural capital depletion and contributes to economic growth and job creation. Business is the driver of innovation, but governments need to provide clear and stable market signals, e.g. through carbon pricing. This report explores policy actions for the deployment of new technologies and innovations as they emerge: investment in research and development, support for commercialisation, strengthening markets and fostering technology diffusion. Competition will be essential to bring out the best solutions. |
|
|
Better Policies to Support Eco-Innovation This new report discusses policies to support eco-innovation in a variety of national contexts and factors such as market structures and dynamics. This work builds on a review of policies to support eco-innovation in OECD countries. It builds on studies of selected eco-innovations: CCS, CHP and fuel cell, electric cars, biopackaging, solar tiles; it highlights different patterns of development across countries. It also presents selected public-private partnerships to support eco-innovation (Sustainable Development Technology Canada in Canada, the Carbon Trust in the UK). |
- Presentations from the OECD/EC/Nordic Innovation Joint Workshop "The Future of Eco-Innovation: The Role of Business Models in Green Transformation" (January 2012, Copenhagen, Denmark)
- Workshop on green growth in Seoul on 4-5 March (March 2010, Seoul, Korea)
-
Point of view: Innovation is the key to green growth (A. Wyckoff, April 2010)
-
OECD Policy Brief “Sustainable Manufacturing and Eco-innovation: Towards a Green Economy” (June 2009) / Synthèses de l'OCDE : "La production durable et l’éco-innovation au service d’une économie verte" (octobre 2009)
-
Presentations from the International Conference on Sustainable Manufacturing (September 2008, Rochester, NY, United States)
OECD websites
- OECD Innovation Strategy
- OECD Green Growth Strategy
- OECD Global Forum on Eco-Innovation
- Environmental Policy and Technological Innovation
- Environmental Policy and Firm-Level Management
- ICTs and the Environment
- Bio-based Economy and Environmental Biotechnology
- STInano
- Household and Public Sector Consumption and the Environment
- IEA Energy Technology Perspectives
External links
- US Department of Commerce Sustainable Manufacturing Initiative and Public-Private Dialogue
- Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), The Key to Innovation Creation and the Promotion of Eco-innovation (Japanese only, English summary available on request)
- EU Eco-Innovation Action Plan
- EU Eco-Innovation Observatory
|
Contact |
OECD Directorate for Science, Technology and Industry
Structural Policy Division
Email: ecoinno [at] oecd.org
Permanent URL of this page: www.oecd.org/innovation/green
Related Documents