Regional Statistics
Metropolitan areas in the world
|
The OECD, in collaboration with the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission, has developed a method to estimate the boundaries of metropolitan areas worldwide, using globally available gridded data at the scale of one km2. |
|
> Read policy highlights here |
||
| |
|
|
||
|
What is a metropolitan area? |
||
|
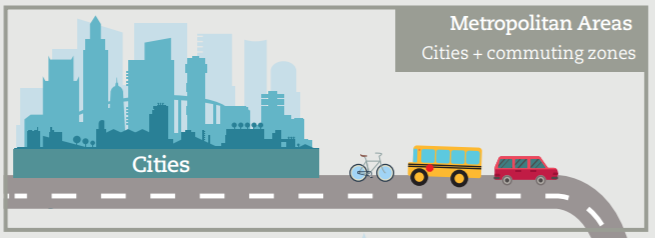
Metropolitan areas are defined relying on the concept of Functional Urban Area (FUAs), which are composed of a city plus its surrounding areas approximating the extent of the city’s labour market (‘commuting zone’). The world delineation of metropolitan areas – aka estimated Functional Urban Areas, eFUAs – relies on globally available gridded data and does not require information on commuting flows and on the digital boundaries of local units. Thus, metropolitan areas are aggregations of grid cells and their boundaries are not adapted to local administrative units or statistical enumeration areas. |
The metropolitan area of Medellin, Colombia
|
|
What method to delineate metropolitan areas worldwide? |
|
|
||
|
Metropolitan areas (eFUAs) have two components: |
|
The method delineates about 9,000 estimated functional urban areas of at least 50,000 inhabitants, worldwide. |
||
| Cities (or urban centres): densely populated areas with at least 50,000 people and 1,500 inhabitants per square kilometre. They are defined using GHSL data and are consistent with those provided in the Urban Centre Database, by the joint researh centre of the European Commission | Commuting zones: areas surrounding cities, socio-economically integrated to the city. The method combines a functional and a probabilistic approach and it relies on a probabilistic approach – performed through a logistic regression model – which is trained using information on actual FUA boundaries in OECD countries. | |||
Related Documents